Buying or selling a used car can be tricky and requires careful planning. Whether you’re looking to buy a used car or sell one, it is essential to understand the market. One should know how to check if the car is in good condition and know the price markup. Both buyers and sellers need to be well prepared to ensure they get a fair deal to make smarter decisions. But first, let’s learn about the average dealer markup on used cars!
What is Markup on Used Cars?
The markup on used cars refers to the difference between the price a dealer pays for a used vehicle and the price they sell it for, with an average range of 10% to 35%. Automotive Dealerships obtain used cars through auctions, trade-ins, or buying from an individual seller. They set a price for the vehicle, including the repair cost and profit margin. The markup percentage is added to the wholesale cost of the car to decide the selling price.
What Is a Dealer Markup?
Dealer Markup is the additional profit a car dealership charges above the Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP) for a vehicle. The dealer buys the car from the factory and can then make it more costly if he wants to. This difference, in simple terms, is what we know as Dealer Markup. The higher the demand for the car, the higher the dealer will charge.
It is required by law that the sticker on all new cars sold in the United States must display the car’s Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price. The dealer markup is often included as a second sticker price. Sometimes, this markup includes charges for dealer-added items to the car, such as seat protection and pinstriping, nitrogen-filled tires, and undercoating–including VIN, etc. However, with current market conditions, there is barely any room to negotiate with these markups, so they are almost unavoidable at this point.
How Do Dealers Set Used Car Prices?
Dealerships source the used cars for their used car inventory from either customer trade-ins or wholesale dealer Car Auctions, which are the two primary sources, and sometimes directly from wholesalers and other dealerships. No matter what is the source of the used car, the markup on the used car is influenced by multiple factors. The following are the most important ones:
1) Cost of the car at which they bought: Dealers try to buy cars ar wholesale prices and sell them at prices obviously over them.
2) Condition of the car: The condition of car, how well it works and rest of it looks decide what will be its selling price.
3) Popularity of the model:If the popularity of the model is high and the models are less, then obviously the prices are high
4) Market conditions: Dealers mark up their cars as much as the market will bear for that model.
5) Using Price Guides: Dealers use price guides like Kelley Blue Book, Edmunds to evaluate price of the Vehicle.

A buyer can determine whether the dealer is charging too much and how much they should negotiate for the used car, using these factors. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of a used car with high or low markup can help buyers decide which option is best for them.
Aging Policies Affect Used Car Markup
Many dealerships have strict rules for how long they keep used cars. If a car doesn’t sell within 60 days, they often auction it off and replace it with another one they think will sell faster. Turning over inventory quickly is important because the longer a car sits, the lower its selling price. Dealerships use automotive software to track how much interest a car is getting and to adjust their markup on used cars in real time and ease the Car Buying Journey.
Dealers themselves are responsible for not having an aging policy . Bcause if you look the cheapest car prices are actully of those which are in the range of 90 to 160 days. The fact is the longer the car sits in the lot the lower its selling price becomes. There are even software that track car interests and price changes in real time.
What is MSRP, and How Do You Use It?
MSRP is the manufacturer’s suggested retail price before any taxes are applied or the price that the product manufacturer recommends to be sold at the point of sale. At times, informally, it is also called the sticker price. It is the recommended retail price for products like automobiles, appliances, and electronics. It is the price suggested by the manufacturer to the final customer. To sell it successfully, the dealer might negotiate down the MSRP, but they won’t sell it for less than the invoice amount as they would not want to lose money on the sale of that vehicle.
MSRP is considered a starting point of the negotiation for a car deal. It is a common practice to negotiate a price for your car. But if the demand is high for that car, there may not be as much potential to negotiate on that car’s price. Comparing prices at another dealer is sometimes helpful while negotiating down from MSRP.
The MSRP should remain constant across retailers as the product’s manufacturer sets it. It is supposed to reflect all the costs spent on the manufacturing and sales process. Retailers may charge less than the MSRP, but the price charged depends on the wholesale cost. The MSRP is often manipulated to an unreasonable high figure, and it is done so retailers can list it at a much lower sale price and indicate to customers that they’re getting a much better bargain.
What Is MSRP vs. Invoice Price?
MSRP and Invoice Price seem complicated but are quite easy to understand when studied on few aspects:

| Aspect | MSRP | Invoice Price(Dealer Cost) |
| Definition | A factory-set price that car manufacturers recommend dealerships to sell cars for. | The amount the dealer paid the manufacturer for the vehicle. It appears on the invoice sent to the dealer. |
| Display | Displayed on the car’s window sticker, often called the “sticker price.” | It is not visible to customers, but the dealer receives it from the manufacturer on the invoice. |
| Pricing Flexibility | Depending on market demand, dealers can sell for more or less than the MSRP. | Dealers use this price to determine potential profit margins. |
| Market Influence | A higher-demand vehicle can see a more significant difference between MSRP and dealer cost, allowing dealers to charge more. | Lower dealer cost means higher potential for dealership profit, especially if the vehicle is in high demand. |
14 Tips for Getting the Best Deal on a Used Car
Buying a car can be strenuous work, as it requires a lot of planning. It’s essential to have a plan before you look for a vehicle, mainly if it’s used. Any buyer would want the best deal for the car they’re getting. So worry not! We have brought you the best tips for getting the best-used car deals.
1) Research About Dealerships: Investigate and find reviews, ratings, and the automotive reputation management of various dealerships.
2) Stay Objective and Clear-headed: Keep your emotions in check and avoid impulsive decisions.
3) Shop at Month-end: Take advantage of the dealer’s end-of-month sales and get better deals.
4) Understand Average Dealer Markups: Learn about the typical profit margins to negotiate.
5) Know the Invoice Price: Find out the price the dealer paid for the car.
6) Research Prices from Multiple Dealers: Compare prices from different dealerships to find the best offer.
7) Schedule an Inspection: Arrange for an inspection to ensure the condition of the car.
8) Evaluate the Condition and Features: Thoroughly assess the car’s state and available features.
9) Research About Incentives: Look out for available incentives and discounts.
10) Start Low with Negotiation: Begin with a low offer to give room for negotiation.
11) Ask Questions and Get Detailed Information: Inquire about the car’s history, warranties, and financing options.
12) Don’t Hesitate to Back Out: Be prepared to walk away if the deal doesn’t meet your expectations.
13) Read Terms and Conditions: Read the fine print before you even make the purchase that is carefully read the terms and conditions an take your time doint that. The documents should accurately reflect the terms of the deal you agreed to and only then sign it.
14) Certifications: Check if the vehicle is certified and fit to be on the road and has no suspicious history. Make sure the health of the vehicle is checked and how long can it serve you after you buy it.
Top Considerations Before Buying a Used Car
Many considerations need to be made before you buy a used car. It is to ensure that whether your purchase decision will be worth it or not. No one would want to purchase a car that they regret in the future. Following are some helpful considerations one should make:
1) Set a Clear Budget
Figure out how much money you are willing to spend on a car, including other costs such as taxes, registration, insurance, and many repairs it may need. Make sure you stick to your budget to avoid spending more than you can afford.
2) Ask for Vehicle History
Ask for a detailed history of the car. It will tell you if the car has been in any accidents, how many people have owned it, and if there has been any major repairs.
3) Check Car Amenities
Make a list of the features you want in your car, like air conditioning, a good sound system, and safety features. Check to see if they are working properly.
4) Inspect Before Purchase
Check the car out carefully before you buy it. Hire a professional mechanic who can check the problems, if any, for you. Sometimes there may be some underlying conditions such as engine issues that might not be visible to the buyer.
5) Assess Your Lifestyle Needs
Think about how the car fits into your life. Find a car that will fit all your needs and according to your vehicle usage, for example. If you have a big family, you might want to opt for an SUV that fits best.

6) Select Your Financing Option
Look at different ways to pay for the car, such as getting a loan from a bank, or a credit union. Compare interest rates and terms to find the best deal. Make sure you understand all the details before you agree to any condition.
7) Know Your Rights
Know about your legal rights before buying a used car from a Used Car Dealership. This includes knowing if you can return the car if you find any problems, what warranties come with a car, and what you can do if something goes wrong after buying it.
8) Check Insurance & Warranty
Get quotes from insurance companies to see how much it will cost to insure the car. Check if the car has any remaining warranty or if you can buy an extended warranty to cover future repairs.
9) Test Drive
A car might be all good however what matters is how does it feel while being actually used. So take the car on test drive , check if there are any odd sounds, all controls are working or not or any other damages to the interiors and exteriors. Moreover how smooth the car is during the drive also matters a lot.
10) Lifestyle Practicality
Check how practical is the car when it comes to actual use. Do you just want it for leisure or as a family car because that decides what type or the model you actually need. Buy an SUV so that it is spacious enough to accomodate your family and luggage. Or if you can afford a sports car then go for it and you dont really have any family or any other considerations.
12 Factors That Influence Dealer Markup on Used Cars
When it comes to the value of a used car, many factors come into play. These factors can help you make informed decisions when buying a used car. It’s essential to consider all these elements and how they affect the car’s price before making a purchase. Here are 8 elements that affect the dealer markup on used cars:
1) Mileage
This refers to the miles the car has been driven. Cars with lower mileage generally cost more because they are considered to have less wear and tear. They are often seen as more reliable and have a longer lifespan.
2) Condition
This is about how well a car has been taken care of. A car in good condition will usually go for a higher price. Dealers spend money to refurbish and repair cars to improve their condition before selling them.
3) Options and Features
These are extras that come with the car, like leather seats, navigation, and sound systems. Cars with more options and features tend to be more desirable and can be of higher price.
4) Location
Where the car is being sold can affect its price. In cities or regions with high demand for cars, prices can be higher. Local taxes and fees can vary too, affecting the final cost.
5) Color
The color of a car can affect its price. Popular colors like black, white, and silver are often in higher demand, so cars in these colors might cost more than less popular colors such as, red or beige.
6) Brand Model and Reputation
Some car brands and models are known for their reliability, durability, and popularity. Cars from these brands often hold their value better and can be priced higher in the Used Car Marketplace.
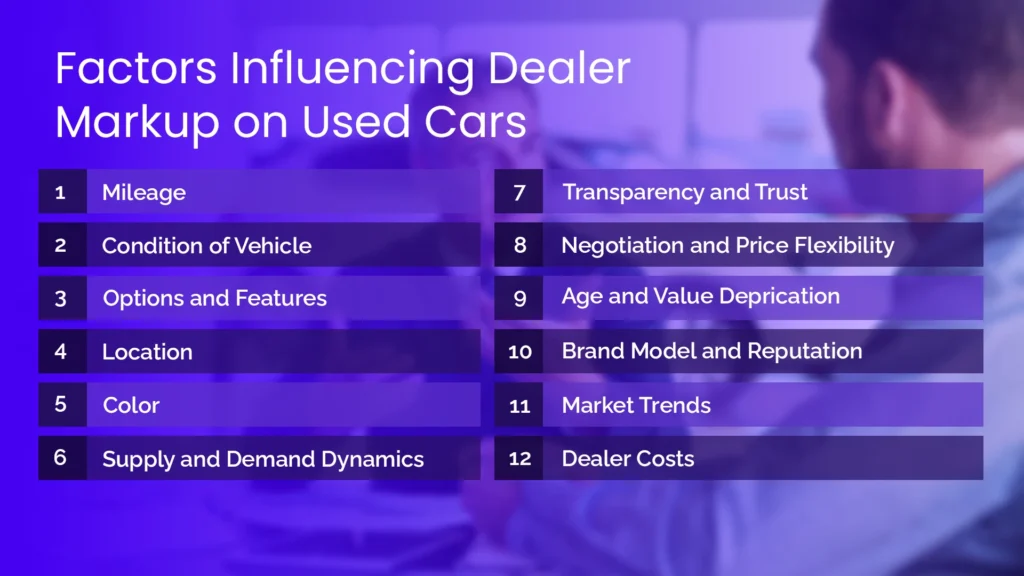
7) Market Trends
Economic conditions and current trends in the car market can impact prices. For example, if there’s a high demand for fuel-efficient cars due to rising gas prices, those cars might cost more.
8) Dealer Costs
Dealers have expenses like buying the car at auction, preparing it for sale, and paying overhead costs like rent and staff salaries. These costs influence how much they mark up the car to make a profit.
9) Supply and Demand Dynamics
The basic economic principle of supply and demand directly impacts the pricing of used car. When a particular type of car model is searched more and is in high demand, however the supply is limited then the prices go high . Similarly if a used car hasnt been sold from a long time and has short interest in it then the prices might be quite low in order to make a sale.
10) Transparency and Trust
It is an important factor in pricing because if a dealer is transparent with its buyer and cimmunicates well all the factors that influence the price and constitute that rate. And also tells about about car history and condition then just on basis of this trust one is open to buy it . THis is because it builds a confidence and improves the overall buying experience for the consumers.
11) Negotiation and Price Flexibility
While it is observed that dealers generally set the prices which are significantly high but it is done in order to make some room for negotiation. So if you are a skilled buyer and has that knack of negotiating then it is easy for you to get to a fair price and also avail additional perks.
12) Age and Value Depreciation
Age and value depreciation are one of the deciding factors because aged cars are generally priced lower because of their older technology and how much they have been already used. Similarly the value also goes down as modern vehicles are priced much higher due to latest technology.
How To Negotiate Dealer Markup?
Negotiating a fair price on a car can be challenging when dealers mark up prices to boost their profits. One should navigate the car-buying process and average markup on a used car to ensure they get a fair deal without overpaying. Give them the best offer based on what they you are willing to pay. They will either accept or they won’t, but you should never go overbound on your budget.
1) Research: Before buying, research the car’s MSRP and follow the Car Buying Guide and compare prices from different dealers to know the fair market value.
2) Know Invoice Price: The invoice price is what the dealer pays the manufacturer. Knowing this can help you negotiate closer to the actual cost.
3) Get Multiple Quotes: Get price quotes from several dealerships to leverage the lowest offer and ensure you’re getting a good deal.
4) Avoid Add-Ons: Skip unnecessary extras like extended warranties and pricey accessories. Focus on negotiating the base price of the car.

5) Look for Manufacturer Incentives: Take advantage of cash-back offers or low-interest financing from the manufacturer to save money.
6) Negotiate Firmly: Be confident in negotiating the price. If another dealer offers a lower price, use it to negotiate a better deal.
7) Watch Out for Fees: Ask about additional fees like documentation or advertising fees, and negotiate them down to avoid unexpected costs.
8) Get Everything in Writing: Once you agree on a price, get a written agreement to avoid any surprises later.
Conclusion
Figuring out how dealers markup used cars involves a mix of market demands, vehicle conditions, dealer costs, and negotiation skills. The Future of Used Car Market is very bright and, both buyers and sellers can look out for easier ways to buy or sell a car. But for now, you can buy or sell used cars by doing your homework beforehand. Being smart and knowing the average dealer markup on used cars, and their ins and outs will help you get a great deal on used cars!