Artificial Intelligence is a revolutionary field of computer science that aims to develop intelligent machines capable of performing tasks that generally require human intelligence. AI has become an important part of our lives, transforming various industries and how we interact with technology. AI has a wide range of techniques, algorithms, and technologies that enable machines to perceive, learn, and make decisions. Also, the applications are vast and diverse. AI represents a transformative technology that revolutionizes various industries and shapes people’s daily lives. It will continue to evolve, and it is essential to harness its potential while ensuring it is used responsibly and ethically.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence refers to developing computer machines that are capable of performing tasks that would generally require human input. As John Mcarthy once said that AI is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines. In simple terms, artificial intelligence is one of a kind technology that can combine computers and datasets, which results in solving complicated problems. These include speech recognition, decision-making, problem-solving, learning, and many more. The major aim of artificial intelligence is to create intelligent machines that can analyze data, adapt to new information, and make informed decisions.

The technology is now applied in most industries. Smart algorithms developed by different companies are now analyzing huge amounts of data to provide effective solutions. AI focuses on cognitive skills and self-learning to improve its results but this technology was not made in a day. It does have a unique history.
A Brief History of AI
The history of ai is unique. AI artificial intelligence has been there in the ancient times, where myths and folklore mentioned mechanical beings with human-like capabilities. However, modern AI emerged during the 1950s when computer scientist pioneers like Alan Turing and John McCarthy actually began exploring the possibility of creating intelligent machines. Significant milestones include the creation of the first program, the development of expert systems, and the birth of various machine-learning algorithms.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence can be categorized in different ways but the most common four AIs are:
- Limited Memory: Limited memory is a kind of machine that has the capability of purely reactive machines and can learn from historical data to make decisions. Applications that still exist in the market right now all come under this category of AI.
- Reactive Machines: This kind of AI emulates the human mind’s capabilities by reacting to different stimuli. This AI is the oldest out of all four. The usage of this AI is limited and can only react to a limited set of inputs.
- Theory of Mind: This AI is the newest form that is still in development. This technology is the newest level of AI. Theory of mind will be better able to understand the emotions and thought processes of the entity it is interacting with.
- Self-Aware: This AI is one that only exists hypothetically. Therefore creating this technology that is way advanced, will be the ultimate objective. This AI technology will be capable of having its own emotions, needs, beliefs, and desires.
How Does AI Work?
AI systems rely on data, algorithms, and computational power to function effectively. They follow several steps, including data acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction, model training, and evaluation. Machine learning which is a component of AI has a crucial role in helping systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time. AI utilizes techniques like machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to achieve its objectives.
Why is Artificial Intelligence Important?
Artificial Intelligence has become increasingly vital in today’s world due to its wide-ranging applications and potential impact on various industries. It is one of the big sources of business innovations.
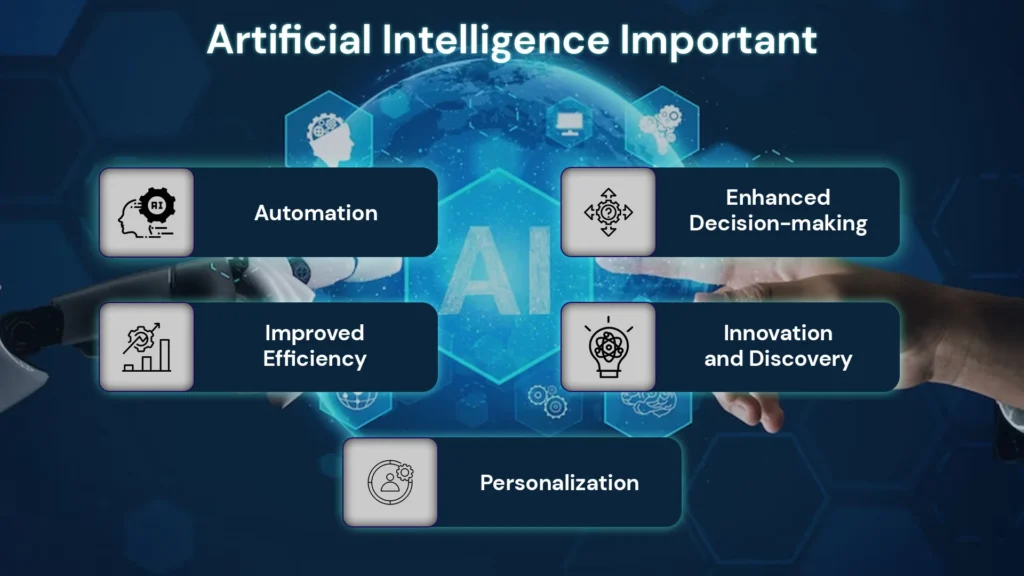
It can help companies achieve objectives in an efficient manner and can make the whole process much easier and simpler. Some of the Importance are:
Automation
AI enables the automation of those tasks that require a lot of repetition therefore, it increases efficiency and productivity. Through machine learning algorithms, AI systems can mimic human behavior, which helps in completing tasks automatically.
Enhanced Decision-making
AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making. This ability provides decision-makers with important information that helps in making quick decisions.
Improved Efficiency
By streamlining processes and optimizing resource allocation, artificial intelligence helps organizations achieve higher levels of efficiency. It can also get rid of inefficiencies, reduce overall costs, and enhance performance.
Innovation and Discovery
AI fosters innovation by unlocking new possibilities and facilitating groundbreaking discoveries. Through data analysis and pattern recognition, AI can understand trends and potential interests. This helps scientists and organizations make new discoveries.
Personalization
AI-powered systems can deliver personalized experiences and tailored recommendations based on user preferences and behavior.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
As with any technology, Artificial Intelligence has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these pros and cons is crucial for responsible AI development and deployment.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
The advantages of AI have a much more overall impact if compared to its disadvantages. The following advantages will help you understand why this technology will help us out in the future.
Increased Efficiency: Artificial intelligence automates tasks, reducing human effort and enabling organizations to achieve higher levels of efficiency.
Improved Accuracy: AI systems can process vast amounts of data precisely, minimizing errors and enhancing accuracy.
24/7 Operations: AI-powered systems can work continuously without fatigue, ensuring round-the-clock operations.
Data Analysis and Pattern Recognition: AI can uncover hidden patterns and insights from complex datasets, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
Risk Mitigation: AI can be used for predictive analytics and risk assessment, helping organizations identify potential issues and take proactive measures.
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Job Displacement: The automation capabilities may lead to job losses in certain sectors, requiring a shift in the workforce.
Ethical Concerns: The ethical implications, such as privacy, bias, and accountability, need to be carefully addressed to ensure responsible usage.
Technical Limitations: AI systems heavily rely on data quality and availability, and their performance can be limited in certain scenarios.
Dependency on Technology: Overreliance on AI systems without human intervention may lead to vulnerabilities and critical failures.
High Initial Costs: Developing and implementing AI solutions can involve significant investments, particularly for small businesses.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to the branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on generating new content, such as images, text, or music, that resembles human-created content. It employs techniques like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to train models that can produce realistic and original outputs.

It refers to a class of AI algorithms that create new content, such as images, videos, or text, based on patterns and examples in existing data. Generative AI systems use techniques like neural networks to generate unique and creative outputs.
Machine Learning Vs. Deep Learning
Machine Learning and Deep Learning are important parts of AI. While they share similarities, they differ in their approach and application.
Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are one of the most common technologies that go hand in hand. Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on developing algorithms and models that enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. It involves training a model on a given dataset and using that trained model to make predictions or perform tasks on new, unseen data. Machine learning algorithms typically rely on statistical techniques to find patterns and relationships in data and make informed decisions.
Deep Learning
It is a subfield of machine learning that specifically focuses on training artificial neural networks with multiple layers (hence the term “deep”) to learn and make sense of complex patterns and representations in data. Deep learning models are inspired by the human brain’s structure and function and can automatically learn hierarchical representations of data. Deep learning algorithms, such as deep neural networks, use layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) to process and extract features from data, enabling them to perform tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
Key Differences are as follows
- Representation of Data: Experts use handcrafted data to work with machine learning. In contrast, deep learning algorithms automatically learn hierarchical representations of the data from raw inputs, allowing them to discover more complex and abstract features.
- Complexity: Machine learning algorithms are generally simpler and rely on fewer layers and parameters than deep learning models. Deep learning models are characterized by their deep architectures with multiple layers of interconnected nodes, which can handle more complex tasks but require more computational resources.
- Training Data Requirements: Machine learning algorithms often require a substantial amount of labeled training data to generalize well and make accurate predictions. Deep learning models typically require even more significant amounts of labeled data due to their more complex architectures.
Augmented Intelligence vs. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
It refers to developing and implementing computer machines that can perform objectives that mostly need human intelligence. Artificial intelligence systems are designed to mimic or replicate human cognitive abilities such as perception, reasoning, learning, and problem-solving. These systems analyze and interpret data, make predictions, automate processes, and perform tasks with varying degrees of autonomy. Artificial intelligence encompasses various technologies and techniques, including machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics.

Augmented Intelligence
Augmented Intelligence, also known as intelligence amplification, refers to using AI technologies to enhance and augment human intelligence and decision-making rather than replacing it. It focuses on leveraging artificial intelligence as a tool or assistive technology to complement human capabilities, enabling humans to perform tasks more efficiently, make better decisions, and achieve improved outcomes. Augmented intelligence systems are designed to collaborate with humans, providing insights, suggestions, and recommendations based on AI data analysis.
Key Differences are as follows
- Relationship with Human Intelligence: Artificial intelligence aims to replicate or mimic human intelligence, often with the goal of automating tasks and replacing human involvement. In contrast, augmented intelligence aims to enhance and amplify human intelligence by providing artificial intelligence tools and technologies to support human decision-making and performance.
- Human-Centric Approach: Augmented intelligence emphasizes the centrality of human involvement and decision-making. It recognizes that humans possess unique qualities such as creativity, intuition, and ethical judgment that are valuable in conjunction with AI technologies. Artificial intelligence, on the other hand, focuses on creating autonomous systems that can perform tasks independently, often with less emphasis on human input.
- Purpose and Goal: Artificial intelligence aims to develop systems that can perform tasks autonomously, learn from data, and make decisions without human intervention. Augmented intelligence, however, aims to enhance human capabilities, improve decision-making, and achieve better outcomes by leveraging artificial intelligence as a supportive tool.
How AI Technology Can Help Organisations
AI technology offers numerous benefits for organizations across various sectors. Some key areas where AI can make a significant impact include:
Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide round-the-clock customer support, enhancing user experience and reducing response times.
Data Analysis
AI can process vast amounts of data quickly, extracting valuable insights that can drive business strategies and improve decision-making.
Automation
Artificial intelligence can automate repetitive and mundane tasks, allowing employees to focus on more complex and creative endeavors. One example is the AI photo editor
Risk Management
Artificial intelligence helps organizations identify and mitigate risks by analyzing patterns and anomalies in data.
Personalized Experiences
AI enables organizations to deliver personalized experiences to their customers, improving satisfaction and loyalty.
Predictive Analytics
It can analyze historical data to make accurate predictions, enabling organizations to anticipate market trends, customer behavior, and demand patterns.
Quality Control
Artificial intelligence can be used for real-time monitoring and quality control, ensuring product and service consistency.
Future of Artificial Intelligence
As technology advances, new innovations can be discovered. Therefore Artificial Intelligence holds immense possibilities and opportunities.
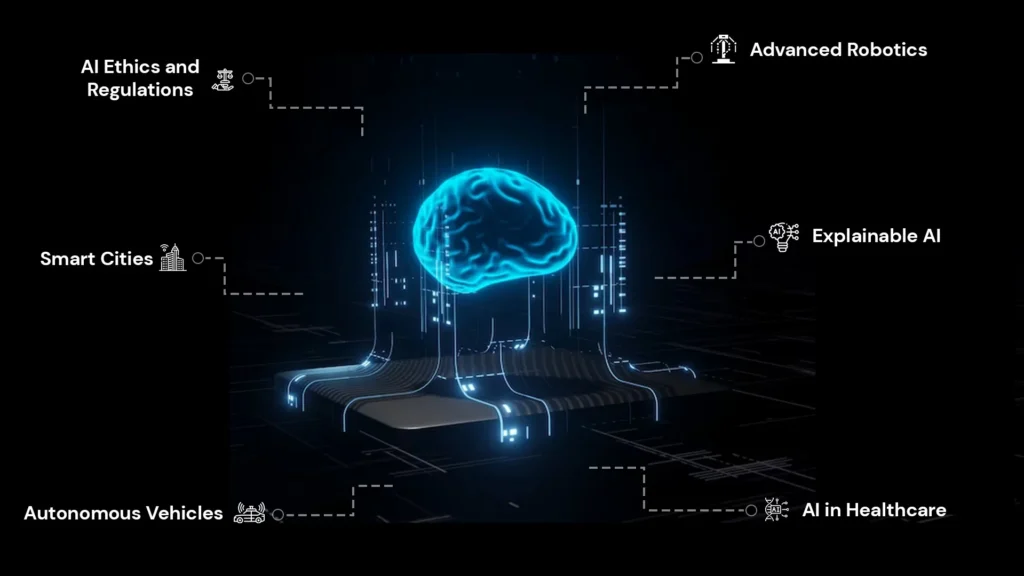
It also has the potential in changing how we interact with other technologies. The implementation of AI in our day-to-day activities has already bought us many advantages. Following are some views that will give us a glimpse of what the future with AI can look like
Advanced Robotics: The integration of AI with robotics will lead to the development of sophisticated robots capable of performing complex tasks.
Explainable AI: Researchers are working on making artificial intelligence models more transparent and explainable to address concerns regarding bias, fairness, and ethical decision-making.
AI in Healthcare: AI will continue to revolutionize healthcare, assisting in diagnosis, treatment planning, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.
Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars and autonomous vehicles will become more prevalent, transforming the transportation industry.
Smart Cities: AI can contribute to building smart cities with intelligent infrastructure, optimized energy consumption, and efficient urban planning.
AI Ethics and Regulations: The ethical implications of artificial intelligence will be a focal point, leading to the establishment of regulations and frameworks to ensure responsible development and usage.
AI Governance and Regulations
As AI continues to advance and permeate various aspects of society, the need for governance and regulations becomes crucial. Governance involves defining policies, standards, and ethical frameworks to guide the development, deployment, and usage of AI technologies. Regulations aim to address concerns regarding data privacy, bias, accountability, and transparency. Governments and organizations worldwide are actively working on formulating artificial intelligence regulations to ensure the responsible and ethical use of artificial intelligence.
As artificial intelligence becomes more pervasive, the need for governance and regulations becomes crucial. Ethical considerations, privacy concerns, and accountability are essential aspects to address. Governments and organizations worldwide are working on formulating policies and guidelines to ensure the responsible and safe use of AI technology.
Conclusion
AI has emerged as a transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize various industries and reshape the way we live and work. From enhancing efficiency and decision-making to enabling breakthrough discoveries, artificial intelligence offers numerous benefits. However, it also comes with challenges, such as ethical concerns and potential job displacement. As we move forward, responsible AI development and governance will play a crucial role in harnessing the full potential of this technology while mitigating its risks.